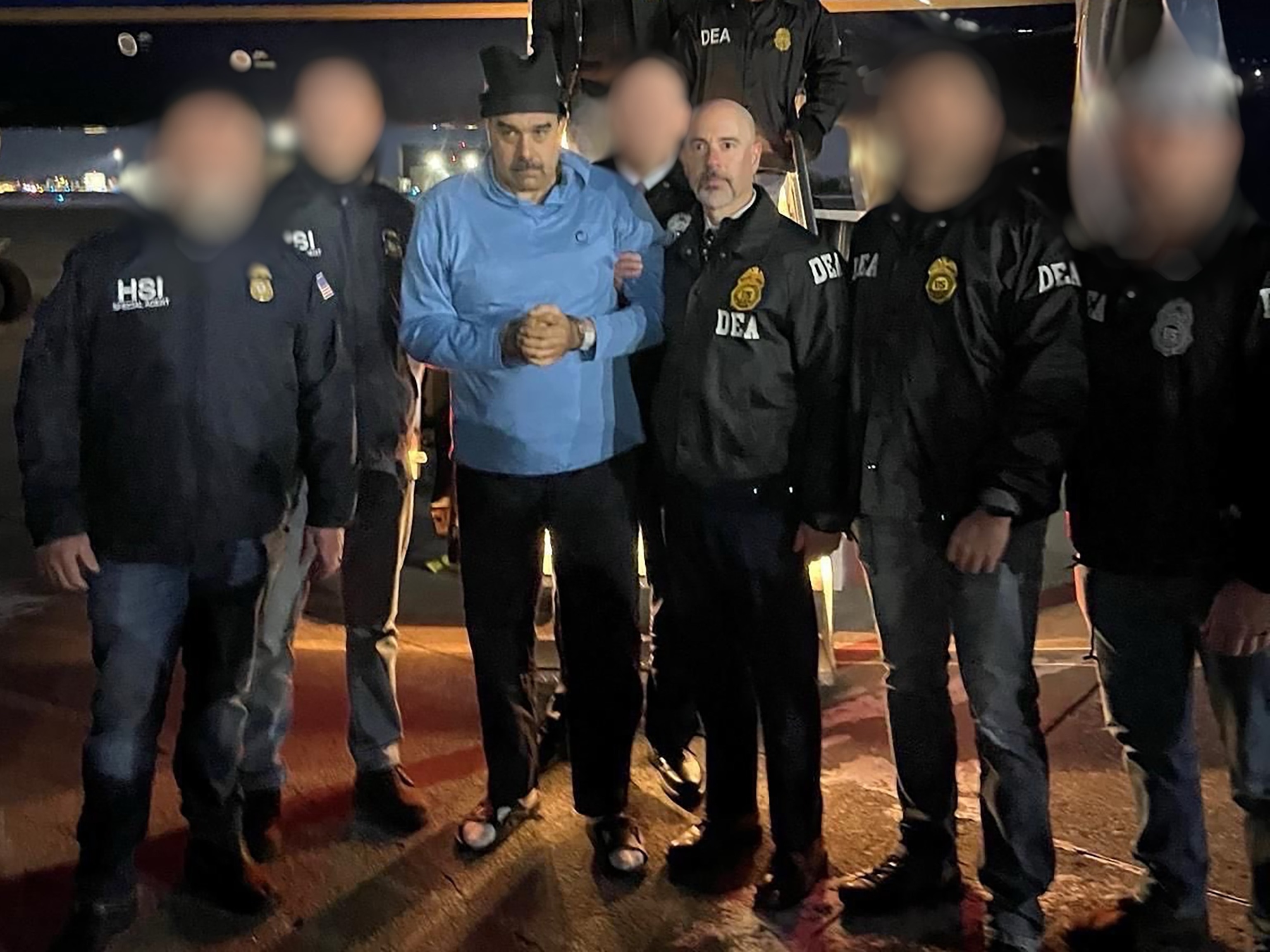
On January 3, 2026, the United States conducted a series of airstrikes on targets in Venezuela, followed by a special forces operation that resulted in the capture of sitting President Nicolás Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores. The operation, described by President Donald Trump as a success in the “war on drugs,” has sparked global controversy, with supporters viewing it as a decisive blow against a narco-regime and critics condemning it as an illegal act of aggression potentially motivated by Venezuela’s immense oil wealth.

Venezuela’s Enormous Oil Reserves: A Key Context
Venezuela possesses the world’s largest proven crude oil reserves, estimated at approximately 303 billion barrels — far surpassing Saudi Arabia’s 267 billion and accounting for nearly 18-20% of global totals. Much of this lies in the Orinoco Belt, a heavy crude region that has been underdeveloped due to sanctions, mismanagement, and infrastructure decay.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Screenshot2024-07-25at7.08.30AM-0ff0b4217f1549eca3397ed636259a03.png)
Visualizations of global proven oil reserves, highlighting Venezuela’s dominant position.
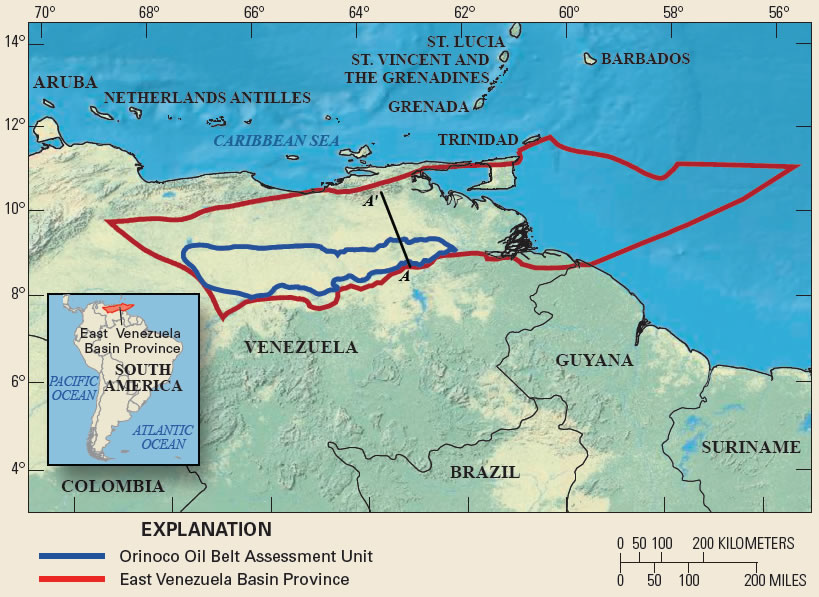

Following the operation, President Trump stated that the U.S. would temporarily “run” Venezuela, with American oil companies playing a central role in rebuilding and modernizing the country’s dilapidated oil infrastructure to “start making money for the country.” Analysts note that restoring production could take years and billions in investment, but the potential access to these reserves has fueled speculation about economic motives.
Official U.S. Reasons for the Intervention
The Trump administration justified the action on several grounds:
- Narco-Terrorism and Drug Trafficking: Maduro has faced U.S. indictments since 2020 for alleged drug trafficking and corruption. The operation was framed as enforcing these charges and disrupting cocaine routes, with groups like the Cartel de los Soles cited.
- Humanitarian and Migration Crisis: Venezuela’s economic collapse has driven millions of migrants to the U.S. border, which the administration linked to Maduro’s governance.
- Illegitimate Regime: The U.S. has not recognized Maduro’s leadership since disputed elections, viewing the action as supporting a transition to democracy.
These align with long-standing U.S. policy, including sanctions and a $15 million bounty on Maduro.
Criticisms and Allegations of Oil-Driven Motives
Many international observers and governments have condemned the intervention as a violation of sovereignty and international law, comparing it to historical U.S. actions but labeling it an act of aggression. Countries including Brazil, Russia, Iran, and others denounced it, with some explicitly calling it “imperialism” driven by Venezuela’s oil resources.

Scenes from global reactions and protests against the U.S. action.
The timing of Trump’s emphasis on U.S. oil companies entering Venezuela has intensified debates over whether resource control was a primary driver, even if not the sole stated reason.
Broader Implications
As of January 4, 2026, Maduro is in U.S. custody facing charges, and the situation in Venezuela remains fluid with reports of unrest and a U.S. military presence. The intervention marks a significant escalation in U.S. foreign policy in Latin America, raising questions about long-term stability, energy markets, and international norms.
This event combines longstanding grievances with new actions, set against the backdrop of Venezuela’s critical role in global oil supplies. The full motivations — security, justice, or resources — will likely be debated for years.
Get Latest News Live on Storify News along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from US News, Trump News, Taylor Swift and Travis Kelce, Kamala Harris, Entertainment, Technology and around the world.
Article Source– https://grok.com/c/282f9659-4e7a-46ea-b976-5faf469ae9a8?rid=c9cd4c92-db74-47dc-bc33-5fece5eb710b
